
For example, consider the same example above with two snowmobiles at a unit cost of $50,000 and a new purchase for a snowmobile for $75,000. The sale of one snowmobile would result in the expense of $50,000 (FIFO method). Therefore, it results in poor matching on the income statement as the revenue generated from the sale is matched with an older, outdated cost.
Excel for Inventory Management: FIFO/LIFO Analysis

In normal economic circumstances, inflation means that the cost of goods sold rises over time. Since FIFO records the oldest production costs on goods sold first, it doesn’t reflect the current economic situation, but it avoids large fluctuations in income statements compared to LIFO. As the price of labor and raw materials changes, the production costs for a product can fluctuate.
Higher Net Income in Inflationary Periods
This method assigns the same cost to each item, by dividing the total cost of goods by the total number of items available for sale. This method retained earnings is also known as the weighted average and is calculated over a specific time period. Simple to use, whether a business or purchasing or producing goods, the end net income is a balance between FIFO and LIFO. FIFO, or First-In, First-Out, is a crucial inventory valuation method in accounting and financial management, especially when considering how to calculate Gross Profit Using FIFO. FIFO (First In, First Out) is an inventory valuation method where your business sells or uses the oldest stock first.
Master the Kanban Inventory Management System for Optimal Efficiency

Manufacturers of vehicles, machinery, and industrial equipment often experience fluctuations in material costs, such as steel and electronics. This is particularly important if the inventory consists of sensitive components or electronics that could be damaged if left too long in storage. Perishables, like food substances, are also handled using the FIFO method. So far, it’s allowed by the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) inside the US, and also for US companies operating overseas. Doing the math might be difficult at first, like every other financial matter. However, we’ll walk you through the steps, and before you know it, the formulas will look quite easy.
Set up barcode scanning to enforce physical FIFO in your warehouse operations. Create a scheduled sync that sends consolidated journal entries with FIFO-calculated COGS to your accounting system. For multichannel sellers, ensure your solution how to calculate fifo can handle FIFO calculations across all sales channels and warehouses for consistent valuation.
- This inventory method is often used in industries dealing with perishable goods, such as food and beverage.
- In addition, consider a technology manufacturing company that shelves units that may not operate as efficiently with age.
- Here’s a summary of the purchases and sales from the first example, which we will use to calculate the ending inventory value using the FIFO periodic system.
- The cost of goods sold (COGS) is calculated as a sum of beginning inventory (opening inventory), purchases during the period, and closing (ending) inventory.
- FIFO is an accepted inventory costing method in the U.S. using Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
- The intelligent financial tools from CalcoPolis would let you calculate all these inventory valuation alternatives in a jiffy.
FIFO vs LIFO: Key differences, formulas and examples
At grocery stores, produce that comes in first is sold first, otherwise, it would perish. Thus, the most recent costs are the ones that remain on the balance sheet while older ones are expensed first. When prices are increasing, companies using LIFO can benefit due to tax purposes.
- This undermines the effectiveness of the FIFO method and can lead to increased waste.
- This leads to higher reported profits, which can be beneficial for attracting investors or securing loans, as the business appears more profitable on financial statements.
- The price on those shirts has increased to $6 per shirt, creating another $300 of inventory for the additional 50 shirts.
- Using LIFO can also result in lower profits on financial statements, which can impact investor perception and business valuation.
- Set up barcode scanning to enforce physical FIFO in your warehouse operations.
FAQs About FIFO Method
FIFO generally leads to higher profits as it improves gross income by selling older, often cheaper inventory first. This method accurately reflects current inventory value, improving profitability in retail environments. To calculate FIFO and LIFO, you will use specific formulas that determine the cost of goods sold (COGS) and ending inventory. For FIFO, COGS is calculated by multiplying the quantity sold by the cost of the oldest items in inventory. Conversely, LIFO calculates COGS by multiplying the quantity sold by the cost of the most recent inventory purchased. You can analyze the FIFO and LIFO in Excel to track stock efficiently and optimize financial decisions.
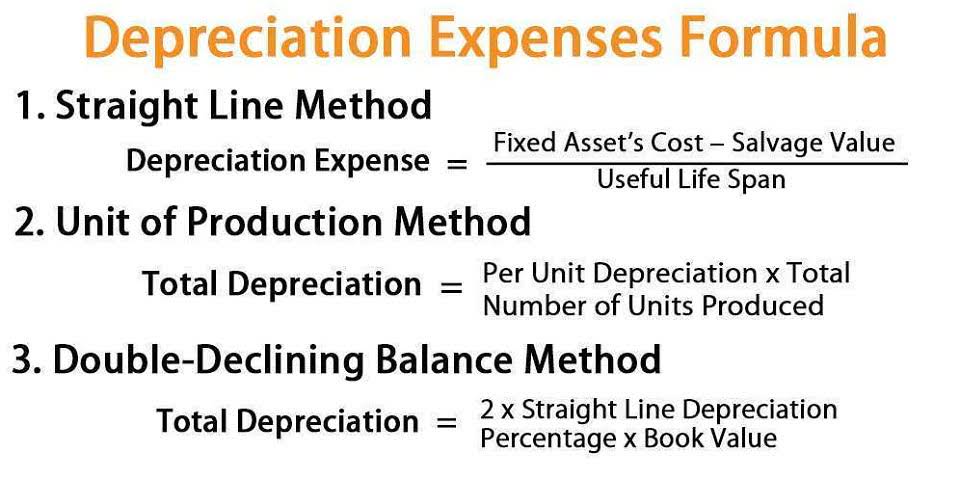
FIFO is an double declining balance depreciation method assumption because the flow of costs of an inventory doesn’t have to match the actual flow of items out of inventory. FIFO lowers COGS during inflation because it first uses older, cheaper inventory costs. This leads to higher gross profit than other methods like LIFO (Last-In, First-Out), which would use the latest, more expensive inventory costs. LIFO can be a strategic choice for businesses looking to reduce taxable income, but it also has limitations depending on accounting regulations and financial reporting goals. FIFO clarifies inventory costs and aligns well with financial reporting standards. LIFO usually doesn’t match the physical movement of inventory because companies are more likely to try to move older inventory first.
These inventory management techniques help maintain the integrity of the FIFO method, even when dealing with large quantities of goods. International financial accounting standards and generally accepted accounting principles often prefer FIFO for its clear inventory accounting and transparent cost of goods sold reporting. First-in, first-out (FIFO) is a method for calculating the inventory value of a company considering the different prices at which the inventory has been acquired, produced, or transformed. Since under FIFO method inventory is stated at the latest purchase cost, this will result in valuation of inventory at price that is relatively close to its current market worth.

